Atropine in ophthalmology has been an essential tool for eye care specialists for decades. Derived from the plant Atropa belladonna, atropine is a potent anticholinergic agent widely used in ophthalmic applications to manage a range of conditions. Its efficacy in dilating pupils and reducing eye muscle spasms has made it indispensable in both diagnostic and therapeutic contexts.
Historically, the uses of atropine in ophthalmology date back to ancient times when belladonna extracts were used to dilate pupil. Today, with modern formulations and refined delivery methods, atropine continues to play a critical role in eye care and treatment.
What is Atropine and How Does it Work?
Understanding Atropine Sulfate
Atropine sulfate is the most commonly used form of atropine in eye care. It is an antimuscarinic agent that blocks the action of acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors in the eye. This action leads to pupil dilation (mydriasis) and relaxation of the ciliary muscles (cycloplegia).
Mechanism of Action in Ophthalmology
When used as an eye drop, atropine in ophthalmology temporarily paralyzes the eye’s focusing mechanism, making it easier to examine internal eye structures. This mechanism also helps manage certain conditions by reducing eye strain and preventing complications.
Common Uses of Atropine in Eye Care
The uses of atropine in ophthalmology span diagnostic and therapeutic needs. Key applications include:
1. Pupil Dilation for Eye Examinations
Atropine is widely used to achieve prolonged pupil dilation, which is crucial for detailed retinal examinations and surgical procedures.
2. Cycloplegic Refraction
In children and patients with accommodative spasms, cycloplegic refraction using atropine helps accurately measure refractive errors by relaxing the eye’s focusing muscles.
3. Managing Myopia Progression
Low-dose atropine has emerged as a proven method for slowing the progression of myopia (nearsightedness) in children, reducing future eye health risks associated with high myopia.
4. Treating Uveitis
Atropine helps relieve pain and inflammation in uveitis by relaxing eye muscles and preventing iris adhesions (posterior synechiae).
Latest Developments in Atropine Treatments
Low-Dose Atropine for Myopia Control
Research shows that low-concentration atropine (0.01% to 0.05%) effectively controls myopia progression in children with minimal side effects.
New Drug Formulations and Delivery Methods
Innovative sustained-release formulations are enhancing patient compliance and treatment outcomes by ensuring consistent drug delivery over time.
Atropine with Other Treatments
Combining atropine sulfate with treatments like orthokeratology shows promise in further improving myopia control results.
Side Effects and Safety Precautions
Common Side Effects of Atropine
- Blurred near vision
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Eye irritation or redness
Precautions for Safe Use
Atropine should be avoided by patients with narrow-angle glaucoma. Care is also needed when using it in infants or elderly patients due to potential systemic side effects like dry mouth and increased heart rate.
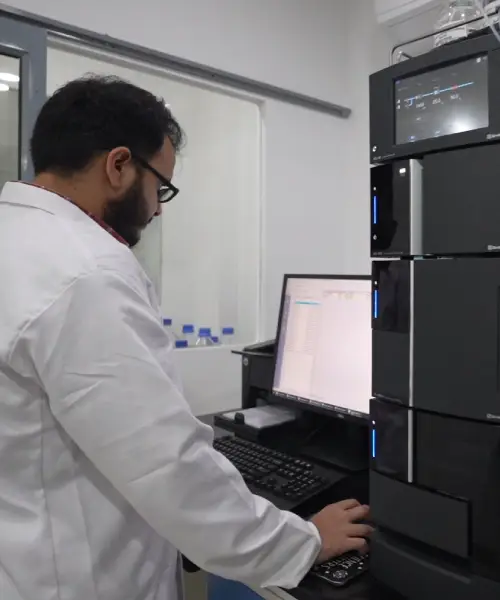
Why Source Atropine from Trusted API Manufacturers?
Sourcing high-quality atropine sulfate is essential for ensuring effective and safe ophthalmic treatments. Partnering with reputable pharmaceutical API manufacturers ensures compliance with international standards, such as USFDA, EU-GMP, and TGA Australia. Reliable manufacturers prioritize quality, transparency, and GMP compliance, ensuring consistent and effective atropine formulations.
Conclusion
Atropine in ophthalmology is crucial for diagnostics, myopia management, and treating conditions like uveitis. Advances in low-dose formulations and delivery systems continue to expand its clinical relevance. Partnering with trusted pharmaceutical API manufacturers ensures safety, quality, and efficacy in atropine-based treatments.